A recent U.S. Navy report finds that per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) concentrated near the runway of the former Brunswick Naval Air Station “may be a primary source of PFAS in (area) groundwater and springs,” potentially contaminating the aquifer that supplies two well fields of the Brunswick & Topsham Water District, which serves roughly 18,000 residents.
The new findings reinforce concerns among community members that persistent chemicals from past military use are migrating off the former base into groundwater and ecosystems.
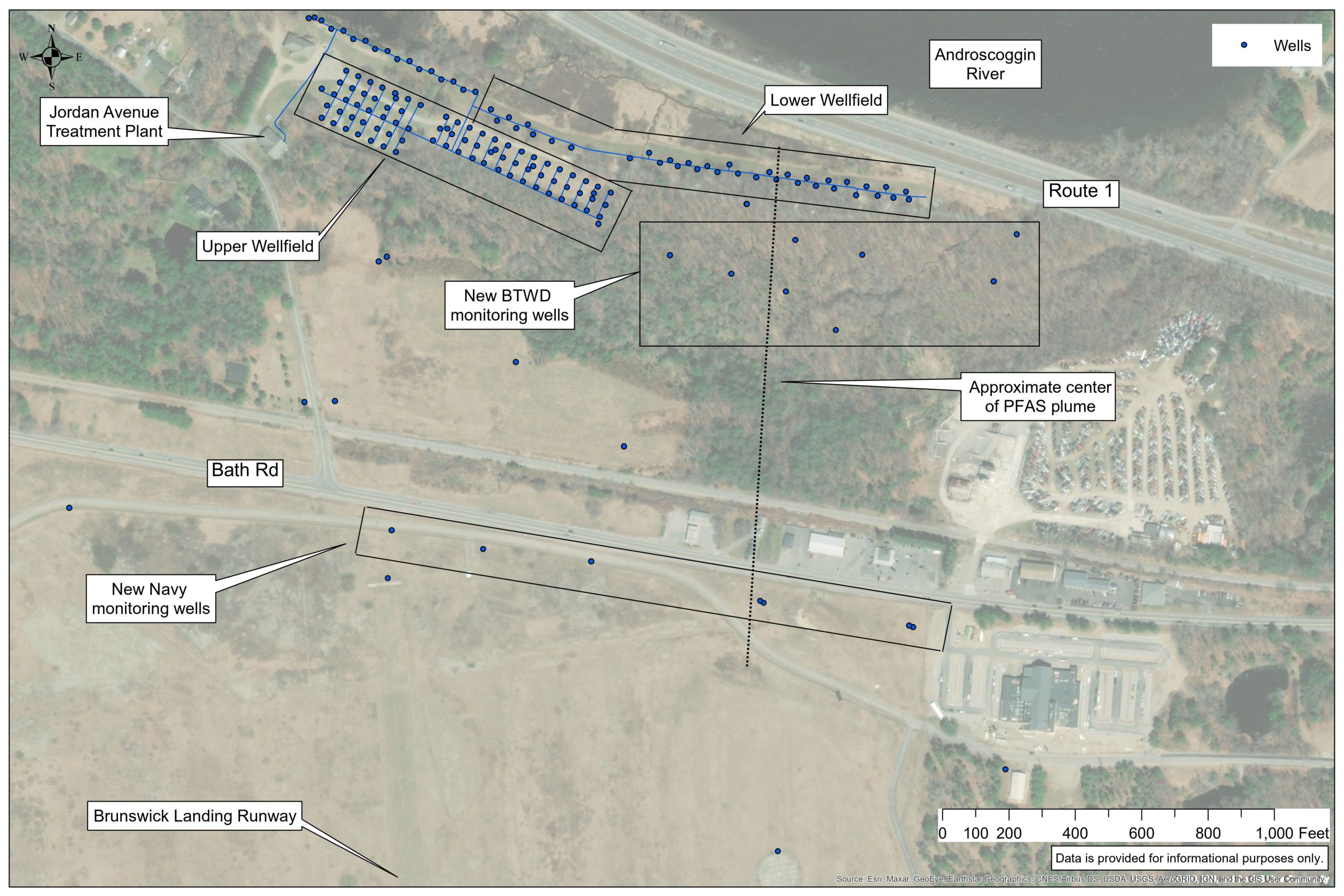
In routine water sampling done last year at its Jordan Avenue well fields, the district found an average PFAS level in its lower well field of 40 parts per trillion (ppt), double the state’s interim drinking water standard of 20 ppt for the sum of six PFAS compounds.
The Jordan Avenue well fields lie roughly a quarter-mile downslope from the northern edge of the former base, and the aquifer that feeds those wells sits partially beneath the end of its runway.

Those two well fields provide a quarter of the district’s water supply. Water from the lower well field has not been used since testing revealed the PFAS, and that lost output has been problematic during the drought, said Craig Douglas, the district’s general manager. If the whole well field had to be taken off-line, the district would likely need to activate an emergency interconnection with Bath to meet peak demands.
The district installed 10 monitoring wells between its well fields and the runway, generating data that indicated the contamination source lay in that vicinity. The Navy also installed 17 new monitoring wells. On Sept. 9, it issued a testing report that showed the highest reading — at roughly 350 ppt for six combined PFAS — came from a deep monitoring well located near a storm drain line by the runway.
“The Navy’s recent testing confirms the presence of PFAS, but it’s not enough to characterize the entirety of the problem,” said Suzanne Johnson, president of Brunswick Area Citizens for a Safe Environment (BACSE), a nonprofit citizens’ group formed in 1990 to support environmental cleanup of the base. “Where are the chemicals coming from and where are they running to? Intensive efforts need to be made now to safeguard the public.”
Containing the Plume
The most prevalent PFAS found in the district’s lower well field testing was PFHxS, or perfluorohexanesulfonic acid. No federal health advisory level has been set for this PFAS compound, but the state of California earlier this year recommended a notification level of 2 ppt for PFHxS, writing that exposure “above certain levels can cause adverse health effects, including harmful effects to a developing fetus, the thyroid, and the liver.”
PFHxS is associated with use of AFFF (aqueous film-forming foam, called “A-triple-F”), which fire departments, airports and military bases began using in the 1960s for fire training and to suppress combustible liquid fires. For decades, AFFF formulas relied heavily on PFAS, mobile chemicals that migrate readily into water systems.
RELATED: The slow path to eliminating PFAS in firefighting foam
When sampling first revealed elevated PFAS in the lower Jordan Avenue field, the district tried to run only its upper well field. But testing in subsequent weeks showed that the lower field’s closure might be driving the contaminant plume toward the upper wells.
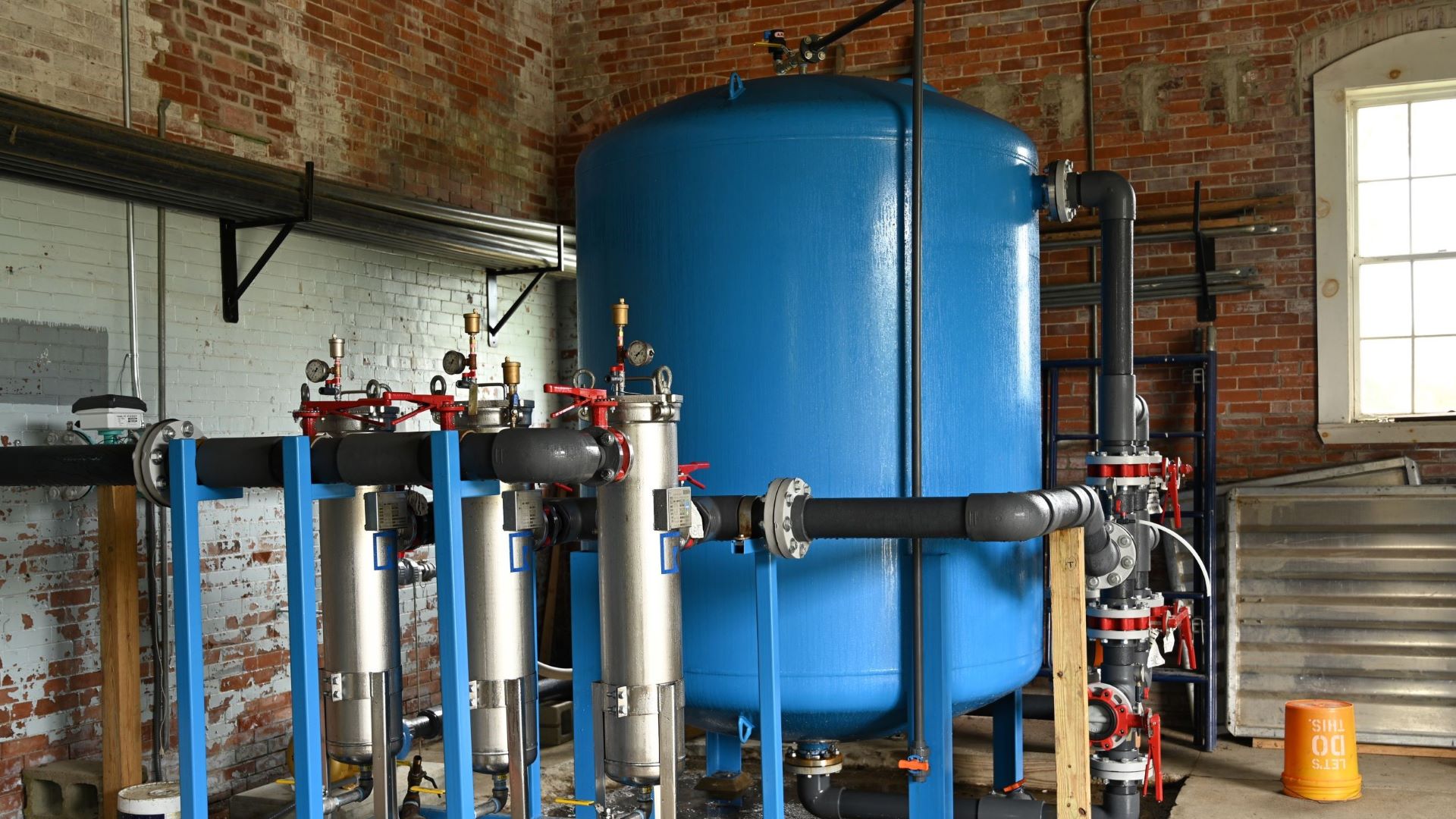
The district quickly installed an organoclay treatment system not designed for long-term use but capable of treating the lower well field water down to non-detectable levels before discharging it back into the ground. That strategy has worked to keep the PFAS plume contained, Douglas said.
District staff are collaborating with the Navy, the Maine Department of Environmental Protection (DEP), the Maine Drinking Water Program, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and BACSE. There’s “a lot of data-sharing, a lot of good science,” Douglas said.
Going with the flow
The most contaminated water sample in the Navy’s recent testing, taken near the runway, came from about 60 feet below ground in sandy soils that lie above a layer of clay. In 1994, hydrogeologists mapped the subsurface soil types and water flows in this vicinity, research that helped guide the recent investigation.
“Hydrogeology is a driving factor of where PFAS go in groundwater,” explained Andrea Tokranov, a hydrologist with the U.S. Geological Survey’s New England Water Science Center. “If you understand the hydrogeology, you’ve gone a long way to understanding where PFAS are moving.”
Tracking that movement is generally easier in a stratified-drift aquifer with sandy material where water tends to move through pore spaces, Tokranov said; bedrock aquifers have fractured flow that Tokranov described as “spider veins” through which water can move unpredictably.
While water movement within aquifers can be mapped, the source of a contaminant plume may remain unidentified, particularly with PFAS, said Chris Evans, a DEP hydrogeologist. “Because it does not degrade, you can have a plume of PFAS without a readily identifiable source [in soil].”
Without a defined soil source, ongoing management of the contamination becomes harder. “If a source is not remediated,” Tokranov said, “you can continuously feed the plume.”
The PFHxS found in monitoring wells and the district’s well field may come from the breakdown of PFAS precursors in the AFFF used decades ago. Ongoing degradation, through microbial action or other processes, may transform chemical precursors into a more stable and enduring PFAS compound like PFHxS, which can then persist for decades, Tokranov said.
“Once you have a large plume,” Evans said, “it’s going to take a very long time for those concentrations to be reduced.”
‘What makes this story so difficult’
Five years before testing revealed the plume, the Brunswick & Topsham Water District had begun sampling for PFAS under an EPA program designed to detect unregulated contaminants in drinking water. (Even today, PFAS remains largely unregulated at the federal level.)
The agency’s early detection program “used a high reporting threshold so compounds were often present in water and detected, but not reported back to EPA,” noted Rainer Lohmann, who directs a federally funded PFAS research center at the University of Rhode Island.
Back in 2016, Douglas said, “there was little awareness of PFHxS and we didn’t have a lab that could detect below 20 ppt.”
The district later undertook voluntary monitoring for 25 PFAS compounds, two years before the state mandated PFAS testing by public water suppliers. The state set an interim drinking water standard last year, and this past June EPA dramatically lowered its drinking water health advisory level for two common PFAS compounds, PFOA and PFOS, from 70 ppt to nearly zero.
“That’s what makes this story so difficult,” Douglas said. “Every few months the PFAS narrative changes.”
Another major challenge is the compounding cost of the routine water monitoring now required to ensure safe drinking water. Each well test costs more than $300 with a 75 percent markup for expedited service. Analysis ordinarily takes six weeks, Douglas said, so to get timely results the district frequently has had to pay the added fees. Between the costs of testing, treatment equipment, monitoring wells and staff time, the district spent more than $386,000 to manage this problem between February and mid-August, Douglas noted.
Those costs are not likely to be covered by the Navy, Douglas indicated, but will be reimbursed by $450,000 in federal funds coming to the district through an emerging contaminant grant awarded by the Maine Drinking Water Program (see box at end of story).
With no effective means to remedy the PFAS plume, the district will need a permanent treatment facility for the entire Jordan Avenue wellfield, Douglas said, an expenditure that comes atop the $30 million it just invested in a new water treatment plant in Topsham. The district is assessing PFAS treatment options but has not determined the installation and ongoing maintenance costs.
“We are working with the Navy,” Douglas added, “to develop an agreement for them to cover construction and operation costs going forward.”

David Barney, the Navy environmental coordinator for the cleanup program at the former Brunswick Naval Air Station, wrote in response to questions from The Maine Monitor that “the Navy, with U.S. EPA and the Maine DEP, is proactively assessing its ability to utilize removal action authority under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (the Superfund program) to address impacts from historical use of firefighting-foam products at the facility.”
Removal actions are typically “interim actions that allow the Navy to respond quickly to environmental conditions, such as PFAS-impacted groundwater” and “could include groundwater treatment or other engineering controls,” Barney noted. “Currently, the Navy is confirming its legal authority to fund a response action at the Jordan Avenue wellfield.”
A bipartisan group of 40 senators, including Angus King, recently wrote Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin criticizing the Department of Defense (DoD) for “not sufficiently prioritizing PFAS testing, remediation and disposal as part of its annual budget process” or adequately planning for further PFAS funding from Congress. Nearly 700 military installations nationwide have known or suspected PFAS contamination.
King, a resident of Brunswick, has already pushed the DoD for further clean-up action, according to the Bangor Daily News. After learning that PFAS contamination in the town’s water supply appears to come from the former Naval Air Station, Matthew Felling, the Senator’s director of communications, noted that thoughts in the Senators’ recent letter “speak to how seriously we want all identified PFAS cases dealt with expediently to reduce the threat to community health.” The Senators called on the DoD “to match Congress’ urgency for addressing testing and remediation by developing requirements-based plans, policies, and programs.”

This project was produced with support from the Doris O’Donnell Innovations in Investigative Journalism Fellowship, awarded by the Center for Media Innovation at Point Park University in Pittsburgh, Pa.








